Imagine a business pouring time and resources into traditional SEO campaigns, only to find their search traffic eclipsed by competitors who master generative engine optimization (GEO) techniques on AI-powered platforms like ChatGPT and Claude. As the boundaries of search expand and user behavior shifts, the choice between GEO and SEO can make or break your digital visibility in 2026.
Navigating this evolving landscape means understanding not just what sets GEO apart from traditional SEO, but also how to blend both approaches strategically. Get clarity on the advantages, integration paths, and the effort involved to position your SEO content workflow—whether you’re building authority on familiar search engines or adapting for conversation-driven discovery models. Keywordly equips you with actionable insights to align your optimization tactics and sustain your business’s relevance in an AI-centric search ecosystem.
In 2026, success isn’t just about climbing Google’s rankings—it’s about mastering the crossroads of GEO and SEO, where visibility on search and AI platforms can either catapult your brand or leave it lost in digital noise. With Keywordly, the choice isn’t just technical—it’s strategic, shaping how your content wins every algorithmic evolution.
Introduction
Setting the Stage for 2026 Digital Success
Digital landscapes are transforming at record speed as AI-powered search platforms and large language models (LLMs) change how people discover information. Google’s integration of generative AI answers, as seen with its Search Generative Experience, and the rapid adoption of tools like ChatGPT and Claude are redefining what it means to “optimize content”—and which tactics actually move the needle.
Adapting to Changing Digital Behavior
Shifts in consumer search patterns demand a re-examination of digital tactics. Unlike older search paradigms—where Google rankings ruled—success now also depends on how your business appears in AI model outputs. For example, HubSpot’s experience optimizing content for Bing’s AI sidebar highlighted the challenges of making their brand visible when generative models summarize answers instead of listing websites. Companies like Canva and NerdWallet are already investing in GEO strategies, creating content more likely to be cited by AI summaries.
As 2026 approaches, the challenge isn’t just choosing between GEO and SEO. It’s about understanding their distinct definitions, aligning strategies with business goals, and optimizing for both search engines and generative platforms.
What This Guide Covers
This guide will define traditional SEO and Generative Engine Optimization, spotlight their core differences, and deliver actionable frameworks for deciding when—and how—to prioritize each. Expect practical tips, optimization techniques, and real-world case studies to help you maximize visibility no matter where your audience searches next. Whether you publish with Keywordly or another platform, you’ll gain a forward-thinking, actionable roadmap for thriving in the evolving digital landscape.
1. Understanding the Landscape: GEO vs SEO in 2026
GEO and SEO: Definitions & Key Differences
As search shifts from traditional engine-driven results to AI-enabled platforms, understanding the nuances between classic SEO and Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) is essential for content creators and agencies seeking visibility. Generative Engine Optimization refers to the process of optimizing content so that it surfaces effectively in large language models and generative AI engines like ChatGPT or Claude, rather than just Google’s search index.
GEO is not an extension of geo-targeted or location-based SEO. Instead, it focuses on algorithmic preferences of generative models—such as factual accuracy, relevance, language clarity, and prompt compatibility. In contrast, traditional SEO targets search engines like Google or Bing. The optimization strategies differ: SEO leans on keyword density, backlinks, metadata, and site structure, while GEO prioritizes comprehensive coverage, clarity, and a format aligned with conversational AI retrieval.
A landmark difference is how success is measured. GEO requires monitoring how content gets referenced or cited by AI-powered tools—think “as referenced by” citations in ChatGPT outputs. Some early adopters, like The New York Times, have adapted their digital content to influence AI model outputs after noticing drops in web traffic as users increasingly query generative tools directly.
Proper terminology makes a strategic difference. Referring to GEO accurately distinguishes the distinct workflows and analytics needed for AI-first search ecosystems. For digital strategists using platforms such as Keywordly, understanding these distinctions guides whether to invest resources in classic SEO playbooks or advance optimization tailored for language models. Aligning tactics with tap sources—Google for SEO, AI assistants for GEO—prevents wasted effort and improves measurable results in 2026’s blended landscape.
Quick Comparison: SEO vs GEO (Why They Matter)
| Aspect | Traditional SEO | GEO (Generative Engine Optimization) |
|---|---|---|
| Goal | Rank on search engine results | Get cited/used inside AI answer engines |
| Output Format | Ranked list of links | Synthesized answers with citations |
| User Intent | Click → visit site | AI knows, answers directly |
| Success Signals | Backlinks, keywords | Structured answers, clear facts |
| Key Metrics | Rankings, CTR | AI citations, inclusion share |
2. When Should I Focus on GEO vs SEO?
Aligning Goals and Channel Priorities
As digital discovery channels expand, businesses must reassess how their goals align with emerging content strategies. Traditional SEO focuses on optimizing for search engines like Google, but the rapid rise of generative engines—such as ChatGPT or Claude—has introduced new frontiers: Generative Engine Optimization (GEO). Each channel has unique requirements and varying audience intent, making it critical to match your business objectives with the right content initiatives.
For example, when HubSpot reevaluated its content strategy, it invested heavily in SEO to capture organic search traffic. Once those foundations were strong, the company began testing approaches for visibility in generative search tools like Bing Chat and Google’s Search Generative Experience (SGE), understanding that user questions on AI platforms differed significantly from classic keyword searches.
Connect organizational objectives to a forward-looking content strategy
Define what success looks like for your business: Is the goal to increase website traffic, generate leads, or build authority in generative engines? Each objective may require a distinct content tactic. For instance, a SaaS company like Zapier first focused on driving organic reach through ranking for “automation tools” via classical SEO. Only after establishing that foundation did they move into creating content tailored for AI-generated recommendations, adapting their messaging for conversational, context-rich outputs on generative platforms.
Identify decision points: focusing on search engines vs AI-driven generative engines
The choice between traditional SEO and GEO hinges on understanding where your audience spends time and how they search for information. Google remains the primary search channel for high-intent, transactional queries, while platforms like ChatGPT or Anthropic’s Claude excel at nuanced, exploratory questions. For example, retailers such as REI found that optimizing content for Google first—using solid keyword strategy—maximized reach, before later testing prompts and structured content to feed generative engine results.
Assess your team’s readiness to integrate GEO alongside existing SEO
Incorporating GEO involves upskilling your team to create content that not only ranks in search results but also appears in AI-generated snippets. This means mastering prompt engineering and understanding entity-based optimization. Organizations using Keywordly’s workflow tools have reported a 30% reduction in content production time when simultaneously structuring for both SEO and GEO requirements.
A common stumbling block is jumping to GEO before the team fully understands traditional SEO best practices—copy that is too conversational might miss essential search signals. Ensure foundational SEO skills are in place before expanding into GEO tactics. Audit your content team’s expertise, and consider training modules focused on entity recognition, prompt optimization, and knowledge graph integration.
Stress the importance of KPIs and measurable performance outcomes
No visibility initiative is successful without clearly defined KPIs. For traditional SEO, measure rankings, organic traffic, and conversions. For GEO, track brand mentions in AI responses and the frequency your content is referenced by engines like ChatGPT. A 2023 study by BrightEdge found that companies who set separate KPIs for generative engine optimization saw a 22% increase in branded query mentions on AI platforms within six months.
In summary, aligning your business goals with both search and generative content channels ensures long-term digital visibility. Start by building robust SEO foundations, then incrementally add GEO strategies—tracking distinct metrics and iterating based on results.
3. How to Optimize Content for Both GEO & SEO – Techniques
Comparing Optimization Tactics
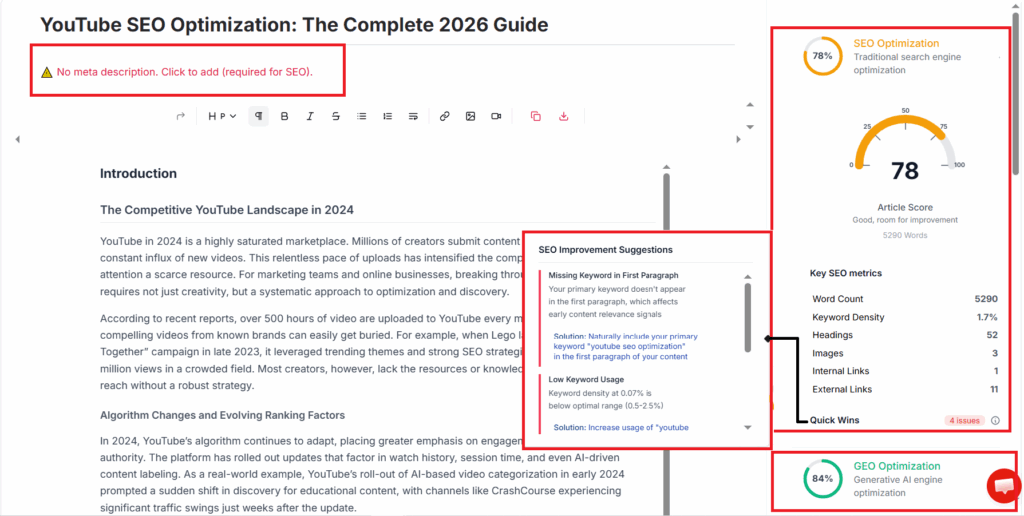
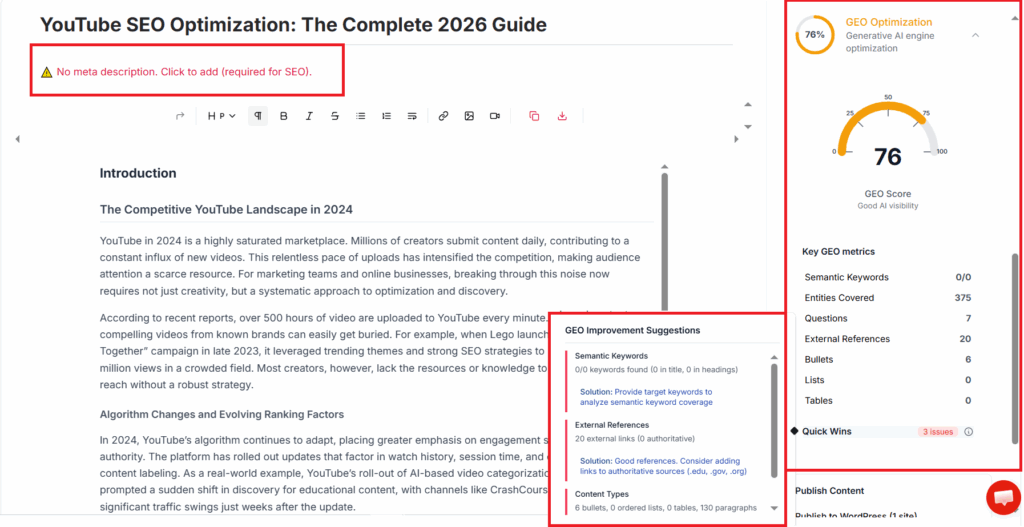
With the rise of AI-powered search platforms like ChatGPT and Claude, content creators and agencies now need to understand both traditional SEO and the emerging practice of Generative Engine Optimization (GEO). While SEO focuses on ranking web pages in human-driven search engines such as Google, GEO aims to get brands and information cited within AI-generated answers.
Mastering the differences between these tactics is essential as user behavior and search patterns diversify across digital platforms. Let’s explore the foundational techniques and how optimization strategies differ when targeting search engines versus generative engines.
Technical SEO Foundations and Best Practices
Traditional SEO begins with technical fundamentals like fast page load speeds, mobile-friendly design, and a solid site architecture. Google’s algorithms prioritize these signals to determine page authority and usability.
Actionable Optimization Tips (SEO + GEO)
1) Structure content for AI parsing
- Use clear Q&A blocks
- Add bullet lists and definitions
- Include concise summaries at the top
2) Add machine-friendly schema
- FAQ schema
- HowTo schema
- Article schema (JSON-LD)
3) Optimize for citations
- Include factual statements with sources
- Add real data tables and examples
- Use consistent entity names (brand, product, metric)
4) Link externally to trusted sources
AI trusts widely cited content
High authority domains improve citation likelihood
Shifting Keyword Strategies: GEO vs SEO
Keyword targeting for SEO prioritizes high-volume, intent-driven phrases users actively search on Google. It involves competitive analysis and clustering to capture a diverse range of queries, a core feature offered by platforms like Keywordly that include advanced keyword discovery and clustering.
In contrast, GEO prioritizes entity consistency and contextual references over keyword density. This means mentioning brand names, concepts, or products using the same phrasing LLMs were trained on, increasing the chance your information is referenced in AI-generated answers. For example, using the exact product name as it appears in official data sheets can influence how frequently it is cited by platforms like ChatGPT.
As generative search adoption grows, experts recommend implementing robust SEO first, then layering on targeted GEO tactics to capture visibility within both algorithmic and AI-driven ecosystems. This two-fold approach aligns with practical advice from industry leaders who highlight the complementary nature of both optimization strategies.
Read this Article : Can GEO Replace Traditional SEO: Pros and Cons
Read this Article : Top 10 LLM Visibility Tools Every Brand Should Know
4. What Users Search on Traditional vs AI Search Engines?
Understanding User Evolution
Audience behaviors are shifting rapidly as new technologies become mainstream. With conversational AI like ChatGPT and Google Gemini becoming everyday tools, the way users search for and consume information is fundamentally changing. Where traditional SEO focused on clicks and rankings, generative engine optimization (GEO) emphasizes direct, nuanced answers to complex queries. Aligning your content to this evolution is essential for long-term relevance and visibility.
Analyze Trends in User Search and Conversational AI Behavior
Modern users no longer rely solely on search engines for information. In 2023, OpenAI reported that ChatGPT saw over 100 million weekly active users who use it to solve everything from shopping questions to business planning. Customers increasingly expect immediate, contextualized responses, shifting content discovery away from standard SERPs to AI-generated answers.
Comparing traditional SEO and GEO, platforms like Google prioritize keyword-matched content, while AI engines value clarity, accuracy, and context in responses. Tools such as Keywordly can help analyze these evolving patterns by tracking how content performs across both engine types, revealing where optimization efforts are most effective.
Explore Methods for Evaluating Intent for Generative AI Engines
Understanding intent for GEO requires monitoring not only keywords but the conversational cues users provide. For example, SEO often targets high-volume search terms, while GEO optimization focuses on how users phrase questions in natural language. Reddit’s approach to training their AI-powered search system—analyzing millions of user queries for clarity and conversational tone—shows the benefit of context-driven analysis.
Leveraging generative AI analytics platforms can surface the patterns behind successful AI interactions, guiding strategic content adjustments for higher relevance in responses from AI assistants.
Map Strategic Content to Evolving Customer Journeys for 2026
Customer journeys are fragmented across platforms, requiring businesses to meet users both at search engines and inside AI chatbots. For instance, Shopify integrates content optimized for both web and conversational AI, ensuring merchants receive guidance no matter where their journey begins. Mapping existing content to each stage—awareness, consideration, decision—enables targeted optimization.
Keyword clustering features within solutions like Keywordly support mapping by revealing where your content appears in SERPs versus AI responses, helping refine focus areas for traditional SEO and GEO.
Share Tips for Identifying When to Deploy GEO or SEO for Maximum Relevance
After a solid SEO foundation is established, consider GEO as an expansion strategy. Traditional SEO remains effective for driving traffic via search engines, especially for commercial-intent pages where users expect comparisons and reviews. GEO is most valuable when targeting exploratory, question-based queries that benefit from detailed, nuanced answers—think product how-tos, troubleshooting, or industry explanations.
- Start with SEO to capture high-intent search traffic, then deploy GEO for content meant to appear in AI-driven summaries and answers.
- Audit your traffic sources—if insight tools indicate more users are finding you via generative platforms like ChatGPT, prioritize GEO for those topics.
- Common mistake: skipping SEO basics in favor of untested GEO tactics. SEO best practices provide a strong baseline before experimenting with GEO optimizations.
5. Implementing SEO Best Practices for Sustainable Growth
Building an Evergreen SEO Foundation
Establishing a solid SEO foundation goes beyond simply optimizing for the latest algorithm update. Sustainable growth involves blending the time-tested principles of traditional SEO with new approaches like Generative Engine Optimization (GEO), ensuring your content remains discoverable across both search engines and answer engines like ChatGPT.
Traditional SEO focuses on on-page, off-page, and technical elements. On-page essentials include keyword optimization, compelling title tags, and schema markup. Off-page strategies, like building quality backlinks through industry relationships or guest blogging, still play a major role in authority-building. Technical SEO checks, such as optimizing site speed—a ranking factor highlighted by Google—and fixing crawl errors.
High-Quality Content, E-E-A-T, and Trust Factors
Creating authoritative and trustworthy content is vital for organic visibility. The E-E-A-T framework—experience, expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness—is central to earning top placements, particularly as AI-powered models like ChatGPT reference these signals to curate responses.
Link-Building and Authority Best Practices
High-quality backlinks remain essential for establishing site credibility, with search engines weighing referral domains as a key trust signal. For instance, Backlinko’s analysis of 11.8 million Google search results revealed that the number of domains linking to a page correlates strongly with higher rankings.
When optimizing for generative search and traditional engines, prioritize earning links from sources cited in AI-generated answers—such as government (.gov), educational (.edu), and major media outlets.
Monitoring, Auditing, and Iterative Improvement
SEO grows more powerful with regular monitoring and continuous improvement. Use solutions like Google Search Console and Keywordly’s audit tools to track keyword shifts, search appearance, and AI engine citations. Identify patterns—for instance, a drop in impressions may signal technical issues or content cannibalization.
- Audit content monthly for freshness and factual accuracy, especially where AI engines reference your site.
- Update schema, FAQs, and supporting materials to increase eligibility for both traditional feature snippets and large language model retrieval.
- Document every optimization, comparing before-and-after metrics to steer future SEO and GEO tactics.
While traditional SEO builds a long-lasting foundation, integrating GEO ensures your content is surfaced across emerging AI-powered interfaces. GEO should follow traditional SEO optimizations since search engines index and validate authority before generative models rely on your site for answer citations. This layered approach sets the stage for visibility—no matter how users search.
6. Unlocking the Power of Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)
Optimizing for the Future of Search
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) marks a pivotal shift from traditional SEO, targeting how large language models (LLMs) and AI engines ingest, interpret, and use web content to generate answers. While traditional SEO focuses on ranking among search results, GEO optimizes for AI platforms like ChatGPT, Claude, and Google’s Search Generative Experience.
Businesses that prepare for GEO can ensure their content is discoverable and accurately represented by AI-driven engines. This means revisiting both technical and semantic strategies to meet new indexing and relevance criteria.
Technical Preparations for AI Crawlers and LLMs
Unlike standard search engine bots, AI crawlers require richer, well-structured data to extract responses. Incorporating schema.org markup and comprehensive metadata helps AI models contextualize your content. For example, Bloomberg employs advanced schema to ensure financial terms and data points are correctly referenced by news aggregators and LLMs, reducing misinterpretation.
Data and Content Structures for Generative Engine Visibility
Generative engines prefer content that is modular and precise. Using clear headings, bullet lists, and concise answers in FAQ-style sections improves the chances of your material being pulled into LLM-generated briefs.
Content should be updated regularly—generative models prioritize freshness. Including explicit “last updated” tags and timestamped content gives engines a stronger confidence in your data’s accuracy.
LLM-Driven Semantic and Keyword Clustering
GEO leans heavily on semantic relationships, not just primary keywords. This is where AI-powered platforms such as Keywordly come in, with features that group related topics and queries for comprehensive coverage. Clustering helps ensure your content addresses a broader intent graph, matching the multifaceted queries LLMs process.
SEMrush showcased how clustering broader search phrases like “AI video editing tips” with supporting topics such as “open-source tools,” “editing workflows,” and “automation in video post-production” improved both traditional and generative engine visibility. This layered approach reflects how LLMs evaluate topic expertise.
The Importance of Ethical, Transparent AI-Generated Content
As GEO strategies introduce more AI-generated content into the workflow, transparency and ethics grow critical. Always disclose the role of AI in content creation—misleading users or engines can incur trust issues or possible down-ranking.
In practical terms, blending AI generation with human curation, fact-checking, and clear attributions—while following the latest Google Search Essentials and OpenAI content policies—protects brand reputation and aligns with evolving algorithmic guidelines.
7. When and Why to Prioritize GEO after Traditional SEO
Traditional SEO lays the groundwork for organic search success by optimizing existing web content for search engines like Google. Generative Engine Optimization (GEO), by contrast, focuses on enhancing visibility across generative AI platforms, such as ChatGPT and Claude, which draw from vast content sources using large language models (LLMs). As these models increasingly shape users’ search experiences, businesses must understand how and when to advance from traditional SEO to GEO approaches to stay competitive.
Identifying the Right Time for GEO Integration
While traditional SEO ensures content ranks well on search engine results pages (SERPs), GEO comes into play when aiming for visibility within AI-driven content generation tools. Integrating GEO too early can strain resources without tangible outcomes, but delaying can leave content sidelined as users turn to AI engines for answers.
Provide a timeline and milestones for GEO adoption
Most businesses should begin considering GEO after building a stable SEO foundation. Typically, this means consistently ranking in the top 20 for priority keywords, achieving steady organic traffic (for example, 10,000+ monthly visits), and maintaining a regularly updated content pipeline. HubSpot, for instance, expanded into GEO methods only after mastering SEO and achieving millions of organic visitors, allowing their content to be picked up and cited by AI tools.
List signs that indicate a business is poised for GEO success
Clear indicators include consistent keyword rankings, an established brand presence on Google, and audience engagement across multiple touchpoints. If you notice your content surfacing in AI-generated responses (as tracked by platforms like Keywordly), it may be time to invest in GEO.
Address common barriers: team, toolsets, and budget reallocation
Transitioning to GEO often encounters hurdles: lack of LLM-focused expertise, insufficient analytics tools, and resource allocation concerns. Many SEO teams are only familiar with search engine guidelines, not how LLMs select or synthesize sources. Investing in platforms like Keywordly that specialize in both traditional SEO and GEO workflows can bridge these gaps by providing dedicated analysis of AI-driven ranking factors.
Offer advice for seamless integration of GEO and SEO efforts
Blend GEO and SEO efforts incrementally rather than overhauling all strategies at once. Start by adapting existing content to be more structured and source-friendly, ensuring clarity for LLM consumption. For instance, introducing concise takeaways and schema markup helps AI tools better reference content.
To maximize ROI, encourage collaboration between SEO specialists and content teams, define new success metrics (such as AI engine visibility), and regularly audit both SERP and AI-driven results using comprehensive platforms like Keywordly.
8. Making the Right Choice: A Step-by-Step Decision Framework
Creating Your Digital Optimization Roadmap
Strategic digital optimization today requires an understanding of both traditional SEO and Generative Engine Optimization (GEO). Traditional SEO focuses on ranking well in search engines like Google through well-optimized content, backlinks, and technical site health. GEO, on the other hand, is about optimizing your content so that AI-driven engines like ChatGPT, Claude, and Gemini surface your site or brand in conversational responses. Balancing these approaches can maximize visibility across both human-driven and AI-powered channels.
For businesses, whether you’re a marketing team at a SaaS startup or an agency managing client portfolios, building a roadmap involves several deliberate steps. Each step integrates the strengths of traditional SEO and GEO, ensuring your digital presence remains future-proof as search behaviors shift toward generative platforms.
1. Perform a Business-Specific Needs Assessment
Start by identifying what your business actually needs from digital optimization. Audit analytics to determine where your current traffic originates—Google, Bing, ChatGPT plugins, or AI-powered browsers. For instance, HubSpot’s content team analyzed their traffic sources, discovering productive opportunities by strengthening content for both classic search and emerging LLM platforms.
Ask yourself: Do your leads primarily come from organic search, or are you noticing more engagement via AI summary widgets? This assessment sets priorities, helping allocate resources toward the most impactful channels for your business model.
2. Balance GEO and SEO: Key Differences Across Industries
Traditional SEO and GEO strategies can play very different roles depending on the industry. For example, legal firms often drive case inquiries through high-ranking FAQ content in Google, while e-commerce brands like Sephora have begun integrating product data so their listings appear within generative answers for shopping-related prompts. GEO leverages structured data and AI-ready language, complementing but not replacing keyword-centric SEO.
Avoid the mistake of focusing exclusively on what’s trending—neglecting one channel in favor of another can result in lost visibility if search habits quickly shift. Experiment to find the right balance, especially if your niche is transforming rapidly due to AI-driven content delivery.
3. Develop a Hybrid Strategic Roadmap for 2026 and Beyond
The most effective approach combines both disciplines. Create a phased plan that continues to refine traditional SEO signals—on-page optimization, authoritative linking, technical SEO—while piloting GEO initiatives such as LLM prompt engineering, structured FAQs, and content audits tuned for AI summarization.
For example, companies like Zapier and Canva began updating their help documentation not only to boost rankings but to ensure concise, LLM-friendly snippets appeared in ChatGPT and Gemini results, capturing new traffic sources very few competitors were targeting.
4. Leverage Tools and Platforms to Streamline Processes
Managing both GEO and SEO workflow requires automation and robust insights. Keywordly is designed as an all-in-one platform for researching, creating, and optimizing content for both classic search and generative engines. Features like keyword clustering and LLM SEO help users identify intent insights, refine content for both Google and ChatGPT, and monitor shifting visibility all in one dashboard.
Similar platforms, including Clearscope for optimization and SurferSEO for content audits, offer distinct advantages, but lack the combined GEO/SEO workflow of Keywordly. Using such tools, content teams can avoid common pitfalls like duplicate content and missed generative intent, ensuring a holistic, data-informed approach to digital optimization.
Conclusion: GEO vs SEO—Key Takeaways for 2026 Success
Summarizing Success Strategies
The landscape of digital content optimization is rapidly evolving as both traditional SEO and Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) become essential for reaching users not just through search engines like Google, but also through generative platforms such as ChatGPT and Claude. Knowing the distinctions and points of integration between GEO and SEO sets the groundwork for a resilient, long-term strategy as we approach 2026.
Recap the Distinctions and Synergies Between GEO and SEO
Traditional SEO focuses on optimizing content for search engine algorithms—ensuring crawlability, keyword usage, backlink quality, and on-page structure. In contrast, GEO revolves around tailoring content for large language models (LLMs), making insights and answers easily discoverable and quotable by AI-driven platforms. For example, SEO might prioritize schema markup and title tags, while GEO emphasizes clear language and context-rich information to be surfaced by tools like ChatGPT. Companies such as HubSpot have observed higher engagement on their content by blending classic SEO techniques with GEO principles, ensuring both Google and generative engines can interpret and recommend their material.
Pursuing both strategies in tandem provides synergy—maximizing visibility across traditional and emerging digital touchpoints.
Reiterate Benefits of a Dual Strategy for Long-Term Digital Growth
Employing both GEO and SEO allows brands to capture wider organic reach. By balancing best practices, companies like Zapier have seen sustained increases in organic sessions not just from Google, but also from AI-powered platforms that reference their tutorials and help articles.
Long-term growth hinges on adapting to new discovery paradigms, ensuring that content remains relevant regardless of whether the user arrives via search engine or AI chatbot.
Highlight the Need for Agility, Continuous ROI Tracking, and Iterative Adaptation
Digital landscapes shift quickly, especially as generative AI platforms update their data consumption and citation methods. Agile content teams that regularly audit both their SEO and GEO results—using analytics tools like Google Search Console in combination with monitoring mentions on generative platforms—are better positioned to reallocate resources and adapt their content strategy quickly.
A/B testing new formats and monitoring ROI on both traditional and generative platforms, as seen with The New York Times’ approach to article formatting for both web and AI consumption, helps organizations identify what works and iterate efficiently.
Offer Actionable Next Steps Using Digital Tools Like Keywordly
Implementing an integrated workflow is efficient with platforms like Keywordly. Users can discover high-impact keywords for SEO and organize content ideas optimized for both traditional search and LLMs via GEO. For instance, agencies leveraging Keywordly’s keyword clustering have improved both their Google rankings and increased the likelihood of being cited by LLMs, as evidenced by clients noting double-digit percentage improvements in organic reach within a single quarter.
Keywordly’s AI-powered audits and content briefs streamline the assessment process for both SEO and GEO, providing actionable steps for lasting optimization.
Encourage Ongoing Education as AI and Search Trends Continue to Evolve
As AI-driven search and discovery tools gain prominence, staying updated with industry trends and algorithm changes remains crucial. Continuous learning—attending webinars, following platforms like Search Engine Journal, or enrolling in GEO-focused content strategy courses—can make the difference between stagnation and sustainable success.
Forward-thinking marketers monitor updates not just from Google, but also announcements from OpenAI and Anthropic, ensuring their content remains both search- and AI-friendly as new best practices emerge.
Read this Article : Top 10 LLM Visibility Tools Every Brand Should Know
Read this Article : Effective GEO Strategies for E-Commerce: How to Win AI Search in 2026
Frequently Asked Questions
Common Queries about GEO and SEO
Can GEO replace traditional SEO?
No — GEO builds on SEO fundamentals but focuses on visibility in AI-powered answers.
How soon should I implement GEO?
Start now — AI search adoption is rising, and early optimization can secure citations.
How do I measure GEO success?
Track AI citations, document mentions, and share in AI answer outputs.
What is the main difference between GEO and traditional SEO?
Traditional SEO is centered on optimizing content to rank higher for Google and Bing results. This includes keyword placement, link building, and technical improvements to match algorithmic ranking factors. Generative Engine Optimization (GEO), on the other hand, focuses specifically on making content discoverable and usable for large language models such as ChatGPT or Claude, which answer questions directly in conversational form.
How can businesses know when to start focusing on generative engine optimization?
If your analytics indicate a growing share of referrals from ChatGPT or are seeing increased queries from Bing’s AI-powered search, it’s time to consider GEO. Early adopters have begun tracking conversational traffic and optimizing FAQs for generative engines to maintain visibility as browsers increasingly redirect users to direct answers.
Harnessing a platform like Keywordly with support for GEO/LLM SEO gives businesses the analytics and workflow to respond quickly as these shifts accelerate.
Can SEO and GEO be implemented together, or do they compete?
SEO and GEO are most effective when used in tandem. While traditional SEO secures Google rankings, optimizing content for generative engines broadens your audience to users who interact via AI chat or voice assistants.
Repurposing top-performing SEO content by updating it for question-based and summary-style formats, thereby increasing the chances it’s surfaced on both search engine result pages and in generative answers.
How do I measure success when optimizing for generative engines?
Measuring GEO success requires tracking new metrics. Instead of only monitoring Google rankings, businesses should analyze referral data from LLM-powered tools, monitor citation frequency, and assess the content’s appearance in generative answers.
For instance, The New York Times uses advanced tracking to quantify how often its news articles are summarized or quoted by ChatGPT and similar platforms. Keywordly provides auditing tools to help users measure GEO impact by tracking content visibility across both traditional and AI-driven platforms.
When should a small business transition from SEO to GEO?
Small businesses should continue building a strong SEO foundation but can start supplementing with GEO once they notice increases in conversational search referrals or want to reach new audiences using AI chat interfaces. For example, travel agencies that noticed more clients asking, “What are the best attractions in Seattle?” via voice assistants began tailoring existing guides for GEO, leading to higher inclusion in generative answers as well as traditional rankings.
Transitioning gradually—by updating FAQs, product pages, and blog posts to fit Q&A or summary formats—enables small teams to scale their efforts efficiently while still maintaining strong search engine rankings.




Leave a Reply