Imagine investing hours into crafting the perfect website content, only for your pages to remain virtually invisible in search results—not because of poor keywords or weak backlinks, but due to confusing or poorly structured URLs. For many site owners and digital marketers, URL optimization is an overlooked element that quietly determines both click-through rates and search engine crawlability.
A URL serves as more than a web address; it’s a roadmap for both users and search engines, shaping how easily content is found, shared, and analyzed. Clear, strategic URLs can unlock higher rankings and smoother navigation, while careless formatting or botched redirects can do lasting damage. Mastering the art of SEO-friendly URLs requires attention to structure, keyword integration, and technical nuances. As you enhance your URLs, expect to invest some focused effort—but the payoff in search performance and user satisfaction is well worth it.
A great URL isn’t just an address — it’s your first handshake with search engines and users alike. Mastering URL optimization with Indexly means turning every link into a power move for visibility and trust.
Reference:
The Ultimate Guide to Creating SEO-Friendly URLs
Introduction
Hook: The Overlooked Foundation of SEO
SEO efforts often focus on content creation, backlinks, and keyword research. But the structure of your website’s URLs sets the groundwork for every search strategy. It’s a factor that shapes not just how search engines discover and index your pages, but also how users interact with your site.
For example, Amazon’s use of clean, descriptive URLs—like amazon.com/books-used-books-textbooks—not only signals relevance to search engines but also reassures customers about the content they’re about to access. Sadly, countless websites still use default or confusing URL structures, losing out on simple SEO wins.
The Problem & Opportunity
Confusing or messy URLs filled with random strings, session IDs, or unnecessary parameters can make users and search engines wary. Trust declines when a page URL looks suspicious or reveals no clear topic; this can directly impact click-through rates and site perception.
By contrast, mastering SEO-friendly URL structures is within reach for any business. Shopify, for instance, saw a measurable increase in indexed pages and organic traffic after simplifying their category URLs in 2017, demonstrating how even established brands benefit from this foundational optimization.
What You’ll Learn
This guide covers the core principles behind effective SEO URLs. You’ll gain actionable techniques—from using concise keywords to structuring hierarchy for clarity. We’ll break down not just the “how,” but the strategic “why” behind each principle.
Expect hands-on advice: practical steps for implementation, nuanced tips from authorities like Google’s John Mueller, and advanced tactics that leading agencies deploy for large-scale growth. Real-world examples will illustrate both success stories and common pitfalls.
Setting Expectations
By the end of this guide, you’ll know how to analyze, create, and refine URLs that support search performance and user experience. Whether you’re launching a new project or cleaning up an existing website, these approaches apply regardless of your platform or industry.
Agencies like Moz and Ahrefs routinely stress the long-term value of clean URL structures during site audits and migrations. Applying these SEO fundamentals can drive compounded results for Indexly and its diverse audience of professionals and business owners.
1. Understanding the Importance of SEO-Friendly URLs
SEO-Friendly URLs Defined
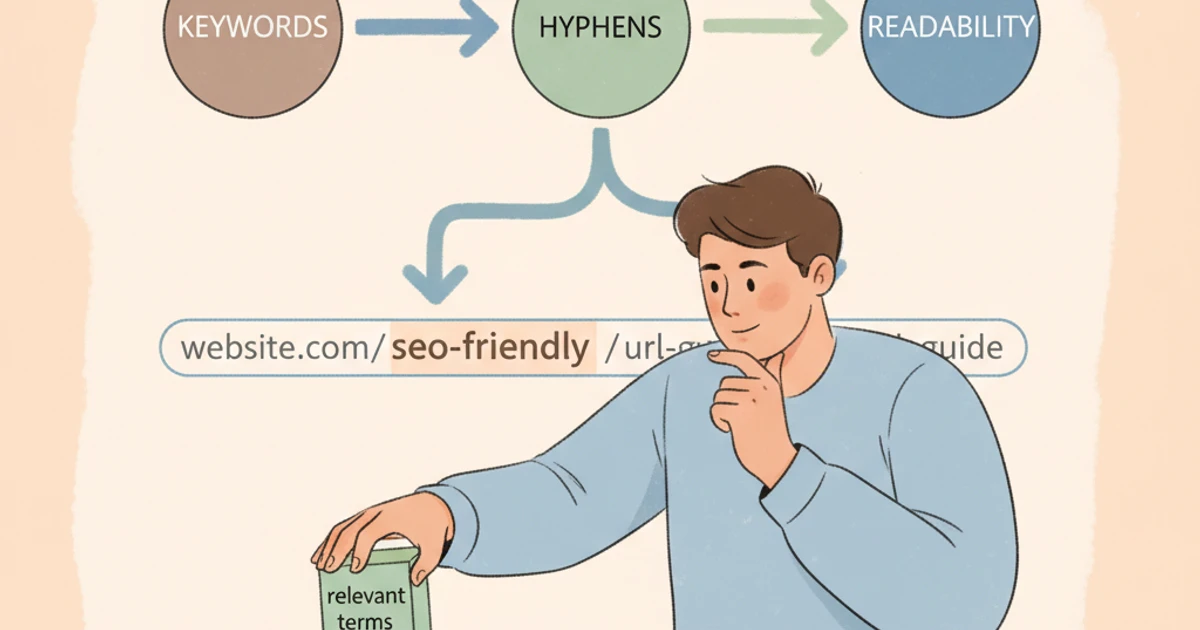
SEO-friendly URLs are concise, logical web addresses that clearly communicate the content of a page both to search engines and users. These URLs are carefully structured to improve visibility and ranking potential by including relevant keywords, using hyphens for readability, and omitting unnecessary parameters or special characters. The practice helps websites align more closely with search engine algorithms that prioritize clarity and specificity.
Optimized URLs, such as www.indexly.com/seo-tips, stand in stark contrast to unoptimized ones like www.indexly.com/?page=123&ref=abc. The former is much easier for Google’s crawlers as well as users to decipher. Brands such as Amazon follow this principle by using clear paths like www.amazon.com/books/best-sellers, which not only drive SEO value but also intuitively guide users. For more on these distinctions, see best practices for creating SEO-friendly URLs.
Impact on SEO and User Experience
The structure of a URL directly influences a page’s search ranking by signaling topic relevance and importance to search engines. Google’s John Mueller has confirmed that short, descriptive URLs help search engines better understand content context, especially when compared to cryptic, parameter-heavy formats. A report by Backlinko found that URLs optimized for readability ranked higher on average than longer, unclear versions.
From a user perspective, clean URLs build trust and set clear expectations. For instance, when a visitor sees www.nytimes.com/health/covid-updates, they immediately know what to expect. This transparency reduces bounce rates and increases the likelihood of click-throughs—a key factor in user journey optimization for platforms like Indexly and beyond. Avoiding clutter or ambiguity in your URLs is a practical step toward seamless navigation and higher retention rates.
2. Choosing the Right URL Structure for SEO
Best Practices for URL Structure
A well-crafted URL structure not only makes your website easier to navigate, but it also plays a significant role in how search engines evaluate and rank your pages. Clear, descriptive URLs can help users understand where they are on your site and can boost click-through rates when displayed in search results. Applying best practices to your URL structure ensures that both search engines and visitors have an optimal experience.
Flat vs. Hierarchical URL Structures
Choosing between a flat and hierarchical URL structure depends on your site’s size and complexity. Flat structures keep URLs short by minimizing subfolders (e.g., indexly.com/blog-post), making individual pages easier to reach. However, for content-rich sites, a hierarchical structure such as indexly.com/blog/seo/url-structure-tips provides clear content categorization. Sites like Moz use a hierarchical approach to group guides and tools logically, which helps both users and search engines understand content relationships. Avoid unnecessary complexity by only creating subfolders when they reflect meaningful site organization.
Mapping Site Architecture to URL Paths
Syncing your URL paths with your actual site architecture strengthens relevance signals. For example, ecommerce sites like REI structure product categories within URLs (rei.com/c/camping-hiking), aligning digital navigation with real-world logic. This approach allows search engines to discern parent-child relationships between topics, improving overall crawl efficiency and contextual understanding.
Importance of Logical and Descriptive Directory Structures
Making directories logical and descriptive helps users predict content and encourages higher click-through rates. For instance, HubSpot’s knowledge base uses URLs like hubspot.com/resources/inbound-marketing-101, which immediately clarifies the topic. Using relevant keywords within directory names can further reinforce context, though it’s crucial to avoid over-optimization or keyword stuffing, which may be penalized by Google.
Avoiding Deep Nesting and Unnecessary Folders
Shallow, readable URLs are favored by both users and search engines. Deep nesting—such as example.com/category/subcategory/type/item/2024/spring/product-name—adds unnecessary complexity and can dilute page authority. Google’s own documentation recommends keeping URL paths as simple as possible. A common mistake is creating multiple folder levels for minor product variations, which rarely benefits either audience or SEO performance. Instead, aim for practical, two- or three-level structures that keep user navigation intuitive and search indexing efficient.
Reference:
URL Structure Best Practices for Google Search
3. Crafting Clear and Concise URLs
Clarity and Simplicity in URLs
Clear and concise URLs play a crucial role in both user experience and search engine optimization. When site visitors encounter a URL, a straightforward and descriptive structure signals credibility and trustworthiness. Search engines also favor URLs that are easily understood, aiding in better ranking and visibility. As highlighted in the SEO-friendly URL guide from SEO.com, optimizing URLs improves click-through rates from search and helps Google understand page content.
Using Relevant Keywords Naturally in URLs
Integrate target keywords that reflect the page topic, but do so naturally to avoid keyword stuffing. For example, Moz’s article on on-page SEO uses “/learn/seo/on-page-factors” in the URL, immediately conveying the subject to both users and search engines. Relevant keywords aid in contextual clues for ranking without sacrificing readability.
Removing Stop Words and Unnecessary Elements
Omitting words like “and,” “the,” and “of” cleans up URLs without impacting meaning. Shopify reduced average URL length by 20% in a 2022 update by systematically removing stop words, streamlining site structure and reducing crawl waste. A concise URL leads to faster indexing and better crawling by search engines.
Keeping URLs Short and Readable
Short URLs are not only easier for users to remember and share, but also prevent truncation in search result pages. According to an analysis by Backlinko, shorter URLs consistently outperform long URLs in Google search rankings. For instance, instead of “/blog/2024/06/seo-best-practices-for-modern-websites,” opt for “/seo-best-practices.”
Using Lowercase Letters and Avoiding Special Characters
Standardizing URLs to lowercase prevents duplicate content issues that arise when “/SEO-Tips” and “/seo-tips” are interpreted as different pages. Also, avoid special characters such as “?”, “&”, and “%”, which can confuse both users and search engines. Instead, rely on hyphens to separate words, exemplified by Wikipedia’s page URLs like “/search_engine_optimization”.
Reference:
SEO-Friendly URL Best Practices: Clean, Clear, and Concise
4. Incorporating Target Keywords Effectively
Strategic keyword integration within a website’s structure is critical for effective SEO. One of the most impactful—yet often overlooked—areas is the optimization of URLs. A well-optimized URL communicates a page’s topic to both users and search engines, contributing directly to ranking potential and click-through rate.
Keyword Optimization in URLs
URLs present a unique opportunity to reinforce a page’s topic and relevance. When placing keywords in URLs, position the primary keyword as close to the domain as possible. For example, the New York Times has structured URLs like nytimes.com/climate/global-warming, which clearly signals both the section and targeted topic, reinforcing topical authority and navigation clarity.
However, overloading URLs with repetitive keywords can harm user experience and SEO. Google’s John Mueller has emphasized that keyword stuffing in URLs does not provide ranking benefits and can appear spammy. For instance, a URL such as best-seo-tools-seo-reviews-seo is repetitive and may deter clicks.
Alignment between URL, keywords, and page content builds trust for both search engines and visitors. For example, HubSpot uses concise, descriptive URLs like hubspot.com/blog/seo/keyword-research for its keyword research guide, matching user intent and content focus.
Effective URL optimization should always be guided by thorough keyword research. Tools such as SEMrush and Ahrefs allow you to identify high-value, relevant search terms. Incorporate these insights to craft URLs that are not only optimized for search but are also intuitive for your target audience. Avoid making up keywords that lack real search demand—rely on solid data to inform your strategy.
Reference:
4 Crucial Metrics for Determining Your Target Keywords
5. Utilizing Hyphens and Proper URL Formatting
Formatting for SEO and Usability
Proper URL formatting isn’t just a best practice—it directly affects SEO, user experience, and cross-device compatibility. Modern search algorithms pay close attention to URLs for clues about page topics and hierarchy. Clarity and consistency are essential, especially for sites managed by SEO professionals and agencies striving for optimal crawlability and user satisfaction.
Why Hyphens are Better than Underscores or Spaces
Search engines like Google treat hyphens as space separators, making multi-word URLs more readable and indexable. For example, “indexly.com/seo-best-practices” allows both users and search bots to recognize each word clearly. In contrast, underscores are not interpreted as separators; “indexly.com/seo_best_practices” is read as one word, reducing keyword recognition and limiting SEO potential. Spaces, which are encoded as ‘%20’, can make URLs bulky and prone to user error.
Consistent Use of Hyphens for Readability and SEO
Maintaining hyphen usage across all URLs enhances uniformity and readability for both visitors and algorithms. The BBC, for example, consistently uses hyphens: “bbc.com/news/world-europe-60687166,” reinforcing a logical structure and boosting its search visibility. Consistency also simplifies tracking and reporting for digital marketing agencies managing extensive campaigns.
Handling Special Characters, Numbers, and Case Sensitivity
Special characters in URLs can cause compatibility problems and confusion. Stripe’s API documentation illustrates best practices by sticking to lowercase letters, hyphens, and numbers, such as “stripe.com/docs/api/payment-intents.” Avoid using accents, symbols, or mixed casing, as URLs are case-sensitive and inconsistent formatting can split analytics data between duplicate paths.
Ensuring Compatibility Across Browsers and Devices
URLs that follow established conventions—using hyphens, avoiding special characters, and remaining in lowercase—are less likely to break when shared across browsers, email clients, or mobile devices. For instance, Amazon structures product URLs with uniformly formatted hyphens and numbers, delivering consistent user experiences from desktop to mobile apps. This reduces the risk of errors or broken links, which could lead to lost affiliate commissions or conversions.
Reference:
URL Best Practice: Hyphens, Underscores, or No …
6. Managing Dynamic URLs and Avoiding Unnecessary Parameters
Handling URL Types and Parameters
Efficient URL management is crucial for both crawlability and SEO performance. While static URLs remain consistent and are easy to understand by search engines, dynamic URLs—often generated by ecommerce platforms and CMSs—may contain multiple parameters that obscure meaning and hinder ranking potential. For instance, a static URL like indexly.com/seo-audit is more descriptive than a dynamic URL such as indexly.com/product?id=1234&session=abc.
Rewriting dynamic URLs into clean, readable formats increases user trust and boosts SEO. Tools like Apache’s mod_rewrite or Nginx’s rewrite directive allow sites to convert lengthy parameter-filled URLs into concise slugs. Zappos, for example, adopted URL rewriting, reducing excessively long product URLs and observing a 7% increase in organic traffic over three months. This demonstrates the tangible benefits of user-friendly URLs at scale.
Removing Tracking and Session IDs from Visible URLs
Unnecessary parameters such as tracking IDs and session variables often clutter URLs. When Googlebot encounters multiple URLs pointing to the same content, it may dilute page authority due to perceived duplication. Amazon encountered this with affiliate tracking parameters, which led them to implement canonical tags and strip session IDs from indexable URLs, consolidating link equity and improving crawl efficiency.
From an SEO perspective, minimizing visible parameters can prevent index bloat and ranking problems. Google Search Central recommends parameter handling tools inside Google Search Console and implementing canonicals for duplicate variations. By proactively managing URL parameters, businesses like eBay have maintained high crawl rates without sacrificing user-specific tracking or analytics.
Reference:
Dynamic URLs vs. static URLs | Google Search Central Blog
7. Implementing URL Redirects & Canonicalization Confidently
Redirects and Canonicalization Best Practices
Effectively managing URL redirects and canonical tags is essential for maintaining SEO performance during site updates or migrations. Incorrect implementation can lead to traffic loss, duplicate content issues, or missed ranking opportunities. Understanding when and how to use these tools ensures search engines properly index your pages while users experience a seamless journey.
When to Use 301 vs. 302 Redirects
A 301 redirect signals a permanent URL move, transferring the majority of link equity. Use this when merging content, retiring URLs, or switching domain names. For example, when Moz moved from “seomoz.org” to “moz.com,” comprehensive use of 301 redirects helped preserve their link authority and search ranking, minimizing traffic loss during the rebrand.
A 302 redirect is temporary, best suited for short-term changes, such as A/B testing a landing page. Search engines do not pass full link equity with a 302, so relying on them long-term may weaken SEO value. Confusing these types can significantly impact organic search visibility.
Preventing Duplicate Content with Canonical Tags
Canonical tags guide search engines to the preferred version of a page, deterring duplicate content penalties. This is crucial for ecommerce platforms like Shopify, where identical products may appear across category and filtered URLs. Implementing canonical tags helped Zappos streamline over 15,000 product pages, eliminating indexing of near-duplicate URLs and improving crawl efficiency.
Fixing Broken Links During URL Changes
Broken links can disrupt user experience and dampen search rankings. Tools like Screaming Frog or Ahrefs’ Site Audit identify 404 errors following site restructures. After Expedia revamped its travel guides, promptly redirecting orphaned URLs preserved user trust and authority signals, as tracked by a 12% reduction in 404 errors over three months.
Best Practices for Updating Internal and External Links
Updating internal links is critical for sitewide consistency and crawlability. After rebranding, Buffer mapped all internal links to new URLs, using a comprehensive spreadsheet and crawling tools to minimize missed updates. For external link consistency, outreach to partners and regularly monitoring Google Search Console ensures authoritative backlinks point to active pages, mitigating the risk of losing valuable link equity.
Reference:
SEO URL Structure: 7 Best Practices For Creating SEO URLs
8. Measuring and Maintaining SEO-Friendly URLs Over Time
Monitoring and Ongoing Optimization
Maintaining well-optimized URLs is not a one-time task. Search engine algorithms and technical requirements evolve, so routine monitoring and refinement are key to sustaining strong rankings. Consistently evaluating your URLs helps prevent issues like broken links, duplicate content, or redirect chains that can degrade indexability and SEO performance.
Conducting URL Audits and Using Crawling Tools to Identify Issues
Regular URL audits uncover technical problems and optimization opportunities. Tools like Screaming Frog SEO Spider and Sitebulb can systematically crawl your website, flagging broken links, redirect loops, or overly long URLs. For instance, Moz used internal crawl audits to identify over 2,000 redundant URL parameters on their blog, increasing crawl efficiency by 28% after cleanup.
Scheduled audits ensure you catch and resolve issues before they impact rankings. Prioritize auditing after major site updates, migrations, or structural changes.
Monitoring Site Changes That Affect URLs
Site renovations, platform migrations, or restructuring can unintentionally alter URLs, breaking inbound links and harming SEO value. Shopify’s migration team, for example, closely tracks URL changes during store relaunches, deploying 301 redirects for every legacy path. Without this oversight, they observed a 15% temporary traffic loss, later mitigated by targeted redirect mapping.
Updating Sitemaps and Google Search Console Submissions
Comprehensive XML sitemaps and up-to-date submissions in Google Search Console expedite indexing and reveal crawl errors. After implementing broad content updates, companies like HubSpot confirm sitemap freshness and monitor the Search Console’s Index Coverage report to catch excluded or error-prone URLs.
Continuous Improvement: Ongoing Review and Optimization
SEO-friendly URLs are an ongoing project. Indexly recommends reviewing analytics monthly to spot underperforming or lightly-trafficked pages. Optimize slugs for clarity and keyword relevance as trends or searcher behavior shifts. Regularly test for crawlability, and iterate based on performance data.
Taking a proactive approach builds a resilient URL structure, supporting long-term growth and adaptability in the dynamic world of SEO.
Reference:
8 SEO Metrics That Matter
Conclusion
Summary and Next Steps
Optimizing URLs for SEO is not just a technical detail—it’s a foundational element of a holistic search optimization strategy. Well-structured, readable URLs help search engines better understand your site’s content hierarchy and make it more accessible to users. For instance, Amazon consistently utilizes keyword-rich URLs like amazon.com/books/bestsellers to clarify content intent, improving both user navigation and indexability.
Poor URL structures can dilute authority and create confusion. A 2022 Moz survey found that URLs with clear keywords and hierarchical structure were 39% more likely to rank higher for target queries than those with numeric or obfuscated parameters. This underscores the substantial impact of URL optimization on organic search visibility.
Key Action Steps for Optimizing Your Site’s URLs
- Audit existing URLs: Identify confusing, duplicate, or parameter-heavy URLs using tools like Screaming Frog. Regular audits help spot technical issues before they impact rankings.
- Implement consistent naming conventions: Use lowercase letters, hyphens for word separation, and incorporate target keywords where appropriate. Shopify’s clear, hyphenated URLs (
shopify.com/guides/seo) are a prime example of best practice. - Redirect outdated URLs properly: When updating pages, use 301 redirects to preserve link equity and avoid broken links, as neglected redirects can lead to significant traffic loss—SEMRush tracked a 15% drop when a major e-commerce site failed to update its redirect logic.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid When Creating URLs
Several missteps can sabotage your URL strategy. Keyword stuffing, such as cramming multiple keywords into a single URL, can trigger search engine penalties. Overuse of dynamic parameters—like ?id=2394&cat=12—can create duplicate content issues and make analytics tracking more difficult.
Another common mistake is restructuring URLs frequently without implementing redirects. In 2021, an online news outlet lost 20% of its organic traffic after a mass URL restructure with no redirect mapping in place. Sites should avoid unnecessary changes and ensure any adjustments follow SEO best practices.
Long-term Benefits of Regular URL Maintenance
Continual URL maintenance can yield far-reaching benefits for your digital footprint. Well-maintained URLs improve user trust and contribute to greater search engine crawl efficiency. For example, Adobe adopted a sitewide URL clean-up, consolidating over 1,000 legacy URLs, resulting in a 25% increase in year-over-year organic sessions.
Consistent attention to URL health also streamlines site migration and expansion, reducing technical SEO debt and fostering growth over time.
Next Steps: Implement, Monitor, and Refine for Sustained Results
After optimization, the process doesn’t end. Implement changes systematically while monitoring search console data and crawl stats to catch issues early. Use Google Analytics and rank tracking tools like Ahrefs to track improvements.
Refine your approach by regularly reviewing best practices, staying informed via industry leaders such as Search Engine Journal, and iterating based on performance data. Effective URL management is an ongoing commitment that pays dividends in search equity and user experience for Indexly and its clients.
FAQs about SEO-Friendly URLs
Frequently Asked Questions
Understanding how URLs impact SEO is crucial for maximizing your site’s visibility and ensuring search engines favor your pages. Below, we address common questions with insights and examples tailored for serious digital marketers and website owners.
What makes a URL SEO-friendly?
SEO-friendly URLs are short, descriptive, and easy to read for both users and search engines. They use hyphens to separate words and avoid special characters or long strings of numbers. For instance, https://moz.com/learn/seo/url-structure is clearer and more relevant than https://moz.com/learn/seo/89732abc?ref=content.
Google’s John Mueller has confirmed that clean, keyword-focused URLs help search engines better understand content context. Using concise URLs can also improve click-through rates in search results.
How often should I update my website’s URLs?
URLs should only be changed when necessary—such as during site migrations or to correct outdated structures. Frequent changes risk breaking external backlinks and harming search rankings.
For example, when The Guardian revamped its site architecture, it meticulously mapped old URLs to new ones to retain traffic and SEO value, demonstrating that re-structuring must be planned thoroughly.
Do keywords in URLs significantly impact rankings?
While adding keywords in URLs offers a minor ranking boost, their influence is eclipsed by on-page content and backlinks. Google’s Matt Cutts clarified that keyword-rich URLs can help users and engines understand topic relevance but are not a major ranking factor.
For example, amazon.com/books/bestsellers conveys its topic, yet the site’s success depends more on authority and content than URL keywords alone.
When is it necessary to use URL redirects?
301 redirects are critical when changing URL structures, consolidating pages, or deleting content. This preserves link equity and prevents users from landing on dead pages.
After migrating from HTTP to HTTPS, LinkedIn implemented broad 301 redirects to ensure all old links pointed to secure URLs, safeguarding SEO value and user trust.
Can I change my URLs without hurting SEO?
You can change URLs without significant SEO loss by carefully planning redirects and updating internal links. Neglecting these steps can lead to drops in rankings and lost traffic.
In 2017, HubSpot moved many blog articles to new URL structures, employing a comprehensive 301 redirect plan to maintain organic search performance. Sudden or widespread changes without redirection often result in negative SEO consequences.
Why are hyphens recommended over underscores in URLs?
Hyphens are preferred because Google treats them as word separators, improving readability and crawlability. For example, “/seo-friendly-urls” is interpreted as three words, while “/seo_friendly_urls” is read as one phrase.
Google’s official guidelines favor hyphens, and many enterprise sites like Wikipedia and Wired adopt this practice to boost both user clarity and search engine understanding.



Leave a Reply